Odds Ratio = (a/c) / (b/d) = ad /bc An Odds Ratio of unity means that cases are no more likely to be exposed to the risk factor than controls Odds ratio in a matched study In a 11 matching, a case is paired with a control based on a similar characteristic (eg age), and the exposure isThe odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/This means that the risk of death after ligation is 63% of the risk of death after sclerotherapy This implies that ligation decreases the risk of death by 37% (calculated as 100 minus 63%) as compared with sclerotherapy The OR for death in ligation group versus sclerotherapy group =

Please Fill Out Table 8 Below Using The Results From Chegg Com
Odds ratio vs relative risk formula
Odds ratio vs relative risk formula-Even an odds ratio; The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
As explained in the "Motivating Example" section, the relative risk is usually better than the odds ratio for understanding the relation between risk and some variable such as radiation or a new drug That section also explains that if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to relative risk and that it has some advantages over relative riskPute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to theThe risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisons by dividing the risk for one group (usually the group exposed to the risk factor) by the risk for the second, nonexposed, group This gives us the risk ratioThe ratio of the risk of healing in the elastic bandage group to the risk in the inelastic bandage group is called the risk ratio For Table 4, the risk ratio = 0538/0284 = 1 The risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RR
Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out toA rate ratio, ;Odds ratio and relative risk




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
The interpretation of an odds is more complicated than for a risk The simplest way to ensure that the interpretation is correct is to first convert the odds into a risk For example, when the odds are 110, or 01, one person will have the event for every 10 who do not, and, using the formula, the risk of the event is 01/(101) = 0091A confidence interval for the MantelHaenszel odds ratio in StatsDirect is calculated using the Robins, Breslow and Greenland variance formula (Robins et al, 1986) or by the method of Sato (1990) if the estimate of the odds ratio can not be determined A chisquare test statistic is given with its associated probability that the pooled oddsLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)




Sas Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logistic Stack Overflow




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = The relative risk is the ratio of the risk in the exposed group to the risk in the unexposed group, as is summarized in Box 1 Depending on the study design and statistical method applied, the relative risk can be presented using different measures of effect, such as the incidence rate ratio and hazard ratio




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Random And Systematic Errors In Case Control Studies Calculating The Injury Risk Of Driving Under The Influence Of Psychoactive Substances Sciencedirect
Relative risk (RR) is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposure Relative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus a non A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2 If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds of an event in the control group




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download
Control Events (E) IE CE Nonevents (N) IN CN The point estimate of the relative risk is R R = I E / ( I E I N ) C E / ( C E C N ) = I E ( C E C N ) C E ( I E I N ) {\displaystyle RR= {\frac {IE/ (IEIN)} {CE/ (CECN)}}= {\frac {IE (CECN)} {CE (IEIN)}}}An odds ratio on the other hand is typically where you select patients based on their disease (or death) status and then explore risk factors for that disease (or death), resulting in a ratio ofThe risk ratio cannot Also, the odds ratio is the basis of logistic regression (used to study the influence of risk factors) Furthermore, the odds ratio is the natural parameter in the conditional likelihood of the twogroup, binomialresponse design Finally, when the baseline eventrates are rare, the odds ratio provides a close




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioRelative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option)The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,




Pdf Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat




Statistics In Medicine Calculating Confidence Intervals For Relative Risks Odds Ratios And Standardised Ratios And Rates The Bmj
Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR = 1 no difference in risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR < 1 lower risk ("protective") in risk of group 1 compared to 2 In our example, p 1 = proportion of women receiving SAT p 2 = proportion of men receiving SAT OR pp pp pp pp = − − = − − 11 22 12 21 1 If you can get a range of plausible risks for the control group, you can work out a range of plausible relative risks The formula is RR = OR / (1 – p (p x OR)) where p is the risk in the control group I've given a readyreckoner table in the BMJ paper And one more subtlety, if IRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
The odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio?About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratioA prevalence ratio, or ; Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of X




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
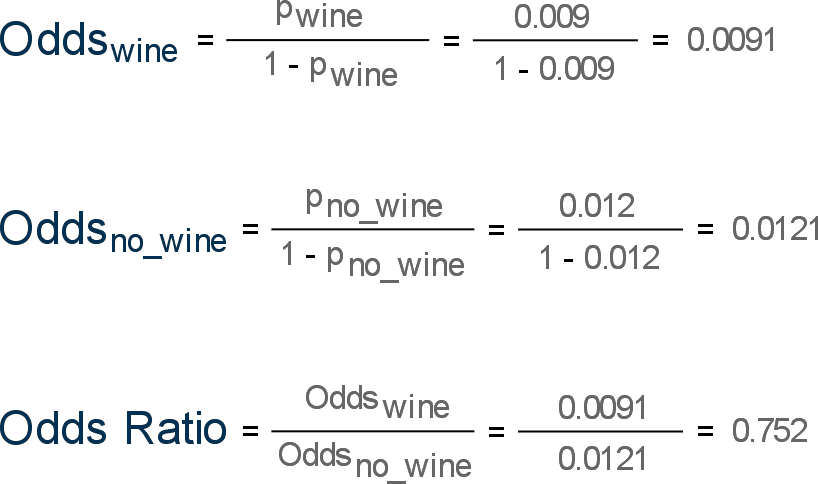
Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 tableOdds ratio (OR) = (a*d)/(b*c) Estimate of population exposure (Px) = c/(cd) Estimate of population attributable risk% = 100*(Px*(OR1))/(1(Px*(OR1))) In retrospective studies you select subjects by outcome and look back to see if they have a characteristic factor such as a risk factor or a protection factor for a diseaseWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR




Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
Abstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Ref=reference category Table A PORs are reciprocals of each other and pvalues are the same regardless of which outcome (yes or no) is modelledEach researcher provides a different method for comparing treatments For example, when the end point is binary, such as disease versus no disease, the common measures are odds ratios, relative risk, relative risk reduction, absolute risk reduction, and the number needed to treat




Community Medicine Psm Odds Ratio Relative Risk Attributable Risk Population Attributable Risk



9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently ( The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab))




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
Therefore, the odds ratio for PONV with Drug X vs PONV without Drug X is 025/067 or 037 The probability of PONV having received Drug X is /100 or 0 The probability of PONV with no Drug X is 40/100 or 040 Therefore, the relative risk for PONV with Drug X vs PONV without Drug X is 0/040 = 05In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Please Fill Out Table 8 Below Using The Results From Chegg Com




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Understanding Absolute And Relative Risk In Medical Risk Analysis And Putting This In Context



Marg Innovera




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Analysis Of Categorical Data
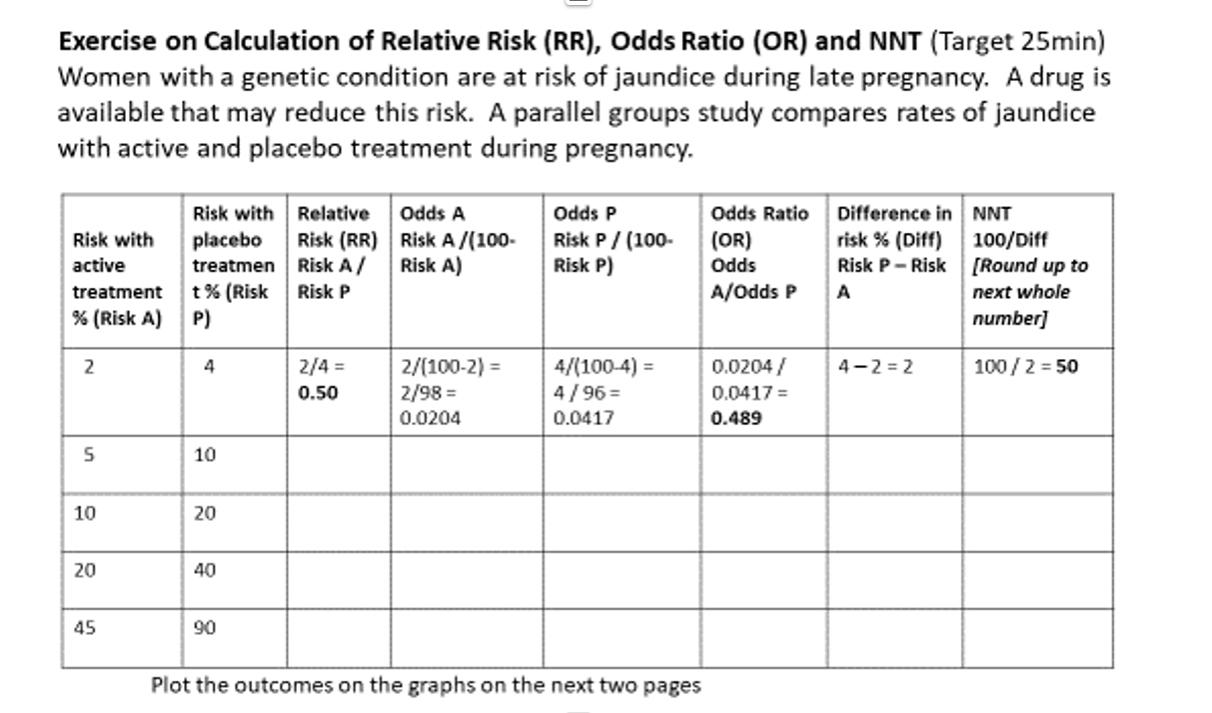



Exercise On Calculation Of Relative Risk Rr Chegg Com




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Risk Difference Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Quantifying Health




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Odds Ratio Article




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Ch 12 Relative Risk Rr Or Flashcards Quizlet




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Bar Graph Represents The Summary Odds Ratios Or Relative Risks Of The Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Rr Definition And Calculation Youtube
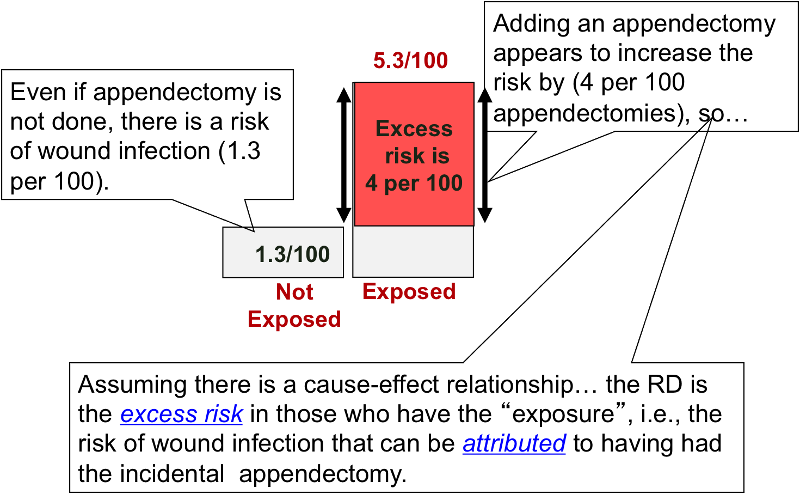



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
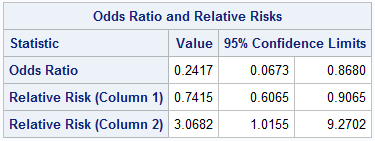



Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice




Measuring Of Risk



Odds Ratio Formula




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



1




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Estimating Risk




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Requesting Effect Measures
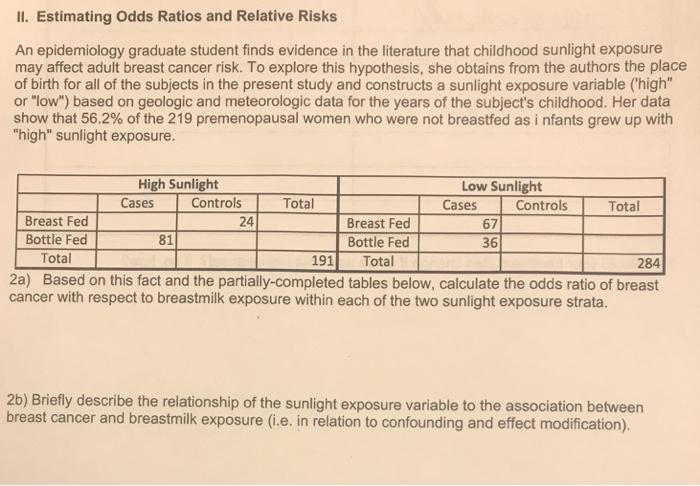



Il Estimating Odds Ratios And Relative Risks An Chegg Com




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
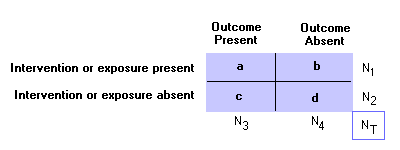



Epidemiology Glossary Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases
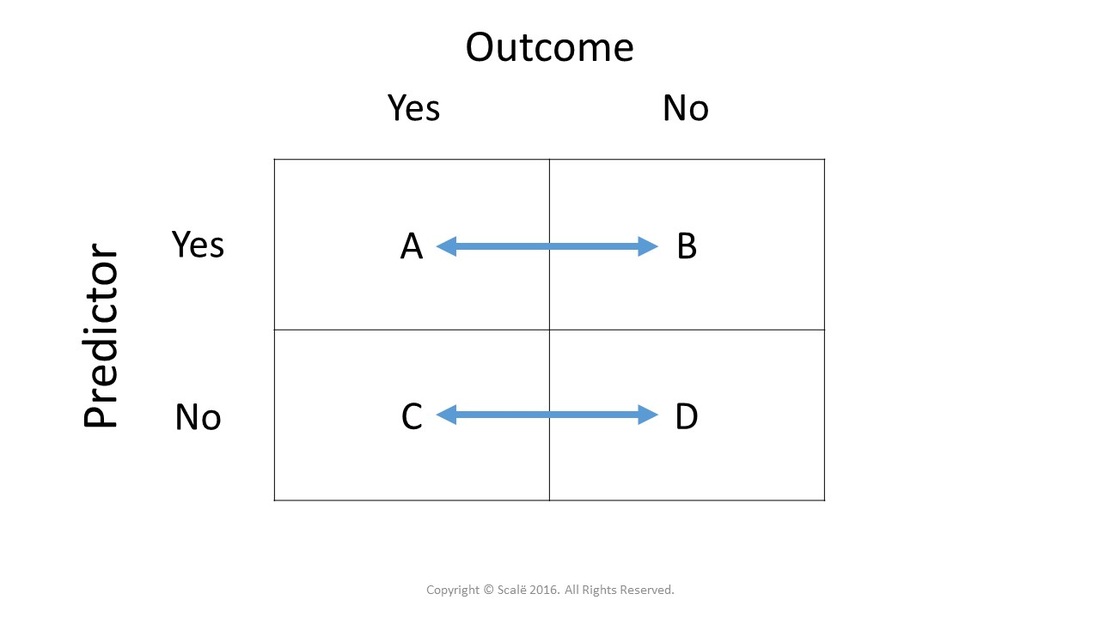



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507



Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram



1
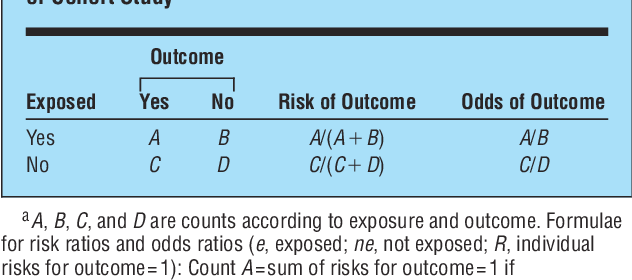



Pdf The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



Relative Risk




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Statistical Notes For Clinical Researchers Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
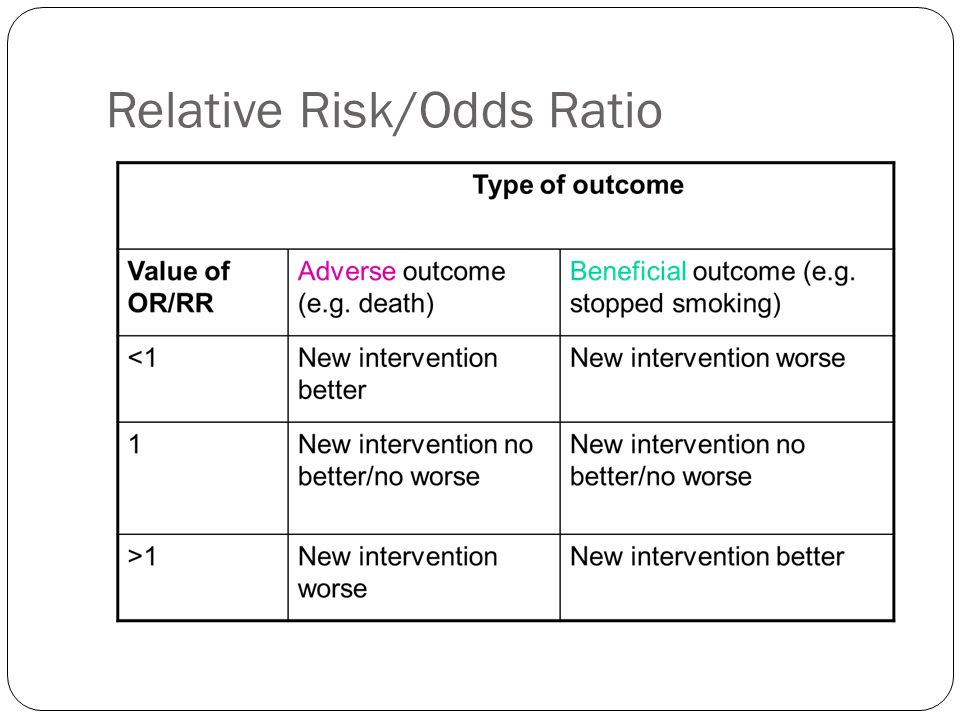



Interpreting Basic Statistics Ppt Video Online Download




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056


